Many folks wonder about the origins of rare health issues, and a question that often comes up is, "Is porphyria from inbreeding?" This query, it's almost like a whisper, pops up because people sometimes link unusual conditions to specific family histories. Today, we're going to talk about porphyria and its actual genetic roots, which are a bit more complex than that simple idea. We will look at what science tells us about how this condition comes about.
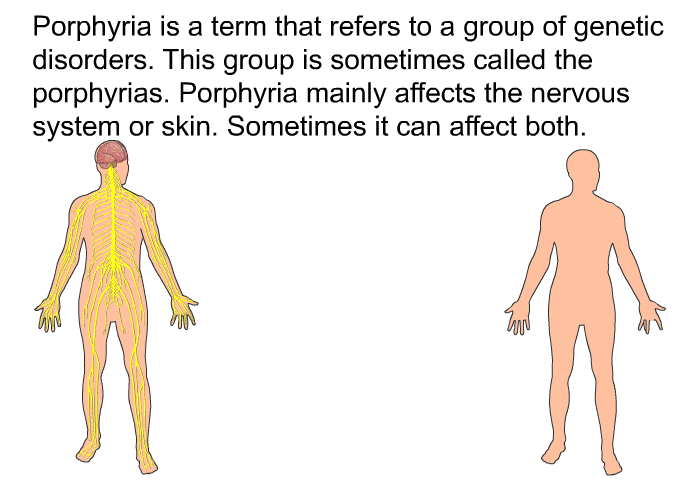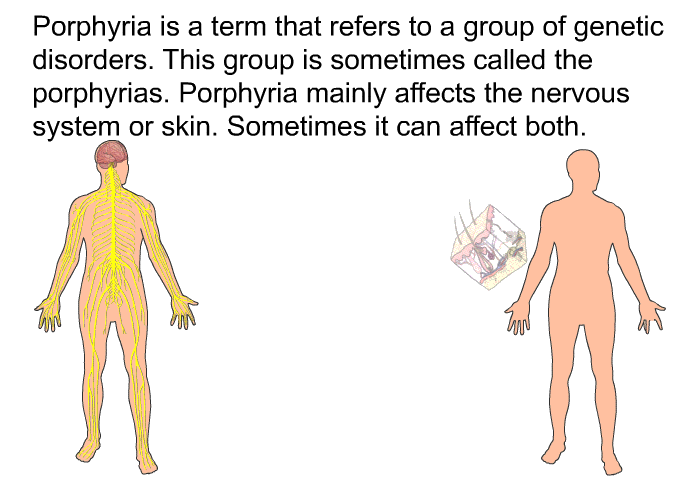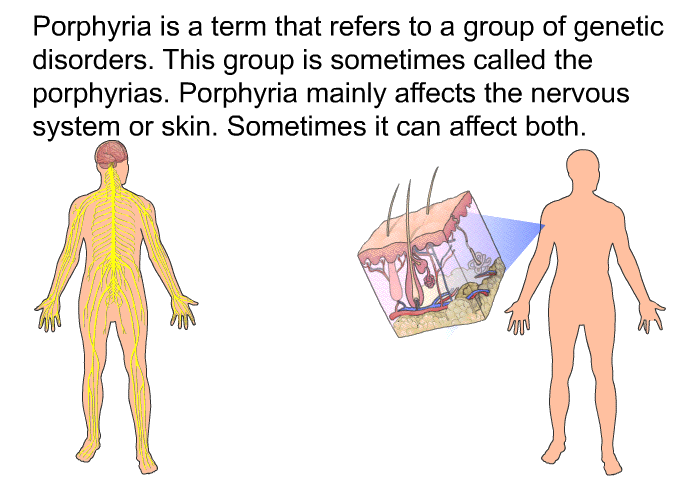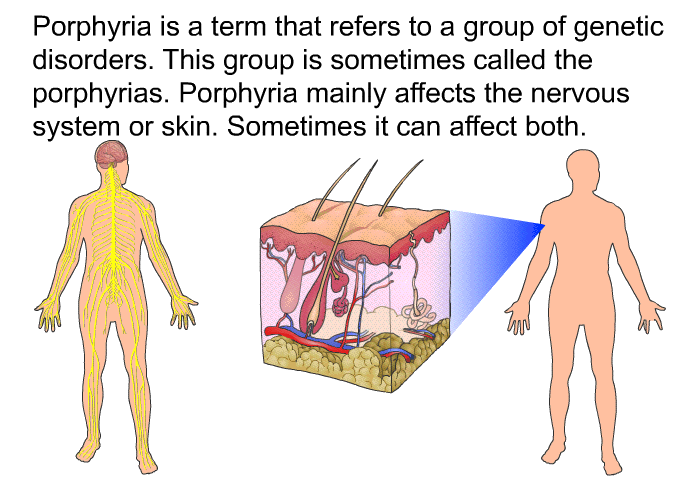
Porphyria, you see, is not just one thing. It is, in fact, a group of rather uncommon disorders. These conditions happen when certain natural chemicals build up in the body. These chemicals are called porphyrins, and they are needed to make something very important: heme. Heme is a part of hemoglobin, the substance in your red blood cells that carries oxygen.
Finding out if someone has porphyria can be quite a challenge. Many of the symptoms of porphyria are very much like those of other, more common illnesses. This means, as a matter of fact, that getting a clear diagnosis can take some time. It is a rare condition, so doctors might not immediately think of it.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is Porphyria?
- How Porphyria Happens: The Role of Heme
- Is Inbreeding a Direct Cause of Porphyria?
- Spotting Porphyria: The Diagnostic Journey
- Treating Porphyria: What You Should Know
- Common Questions About Porphyria (FAQs)
- Where to Learn More
What Exactly is Porphyria?
Porphyria, as we mentioned, is a collection of disorders. These conditions arise when certain natural chemicals, called porphyrins, build up in the body. They are, you know, substances that are part of the process of making heme. Heme is a very important component in our bodies.
When these porphyrins accumulate, they can cause a range of health issues. The specific symptoms depend on the type of porphyria someone has. There are different forms, and each one can show up in a unique way. Some forms affect the skin, while others primarily affect the nervous system.
It is a condition that, in some respects, affects very few people. This rarity is part of why it can be so hard to pin down. Knowing what it is helps us understand why the question about its origins comes up so often.
How Porphyria Happens: The Role of Heme
To understand porphyria, we need to talk a little about heme. Porphyrins are needed to make heme. Heme is a vital part of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in our blood. It is also important for other proteins in the body.
The body has a series of steps, kind of like an assembly line, to make heme. Each step involves a specific enzyme. If one of these enzymes isn't working right, or is missing, the chemicals that come before it in the process can build up. These are the porphyrins.
This buildup is what leads to the symptoms of porphyria. So, in a way, porphyria is a problem with the body's natural chemical factory. It is a metabolic issue, basically, where a process goes awry.
Is Inbreeding a Direct Cause of Porphyria?
Now, let's get to the main question: Is porphyria directly caused by inbreeding? The short answer is no, not directly. Porphyria is a genetic condition, meaning it comes from changes in our genes. Inbreeding itself does not create these genetic changes. What inbreeding can do, however, is increase the chance of inheriting certain genetic traits.
When people who are closely related have children, there is a higher chance that they might both carry a rare, hidden gene change. If both parents pass on that same altered gene, and if it's a recessive condition, their child could then develop the illness. This is how conditions that are very rare might appear more often in certain family lines. But the inbreeding itself isn't the cause; it just increases the odds of inheriting an existing genetic change.
Recent advances in porphyria genetics have given us a much clearer picture. We know more about the inheritance patterns, how often the genes show up, and the different molecular variations. This includes finding new genes that can either cause or change the course of the condition. So, the picture is quite a bit more detailed than just a simple link to inbreeding.
Understanding Genetic Inheritance in Porphyria
Porphyria is passed down through families in different ways. Some forms are inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. This means if you get just one copy of the changed gene from either parent, you could develop the condition. Other forms are autosomal recessive. For these, you need to get a changed gene from both parents to have the illness. If you only get one, you are just a carrier.
The way these genes are passed on is what truly determines the risk. It is, you know, about the specific genetic blueprint. The concept of "penetrance" also comes into play. This refers to how likely it is that someone with the gene change will actually show symptoms. Not everyone with the genetic change will get sick, which is a bit surprising to some.
So, while family connections matter, it's about the specific genes involved. It is not about how closely related the parents are as the sole factor. The genes themselves hold the key.
Familial Versus Sporadic Forms
It is interesting to note that porphyria can show up in two main ways: familial and sporadic. Familial forms mean the condition is passed down through the family, as we just discussed. This means there is a clear genetic link that runs in the family tree.
Sporadic forms, on the other hand, appear without a clear family history of the condition. Porphyria Cutanea Tarda, or PCT, is a good example of this. PCT is the most treatable form of porphyria. Treatment appears equally effective for both the sporadic and familial forms of PCT. This suggests that while genetics play a part, other factors can also trigger the condition in some people. So, it's not always about what you get from your parents, very much not always.
The standard treatment for individuals with PCT is well-established. This is good news, as it means there is a path to feeling better, regardless of how the condition first appeared. It just goes to show, the human body is quite complex, isn't it?
Recent Discoveries in Porphyria Genetics
The field of porphyria genetics is always moving forward. Researchers are constantly finding new things. Recent advances have really deepened our collective understanding of how these conditions work at a molecular level. This includes discovering new modifying or causative genes. This means we are learning more about what makes the condition show up, and what might make it different in various people.
These discoveries are important for diagnosis and for developing new ways to help people. For example, a medication called Givlaari (Givosiran) is now used for adults with acute hepatic porphyria. It is given once a month by injection. This medicine can reduce the number of porphyria attacks. It works because it helps people whose livers lack the enzyme needed to make heme. This is, you know, a very promising step forward in care.
Learning more about these genes gives doctors better tools. It helps them understand why some people get sick and others with similar genes do not. This knowledge also helps us move beyond older ideas about what causes these conditions. It is a constantly evolving area of medical science.
Spotting Porphyria: The Diagnostic Journey
As we have touched on, getting a diagnosis of porphyria can be quite a journey. This is because many of its symptoms are shared with other more common illnesses. It is a bit like trying to find a specific needle in a very large haystack. Because it is a rare disease, doctors might not think of it right away.
If you have symptoms of porphyria, you are likely to start by seeing your primary care provider. They are your first stop, naturally. However, because porphyria can be difficult to diagnose, you may be referred to a specialist. This could be a liver specialist, a hematologist, or even a specific porphyria clinic. I mean, it's not a simple process.
Sometimes, even specialists might have trouble. One person shared that they saw a liver specialist who referred them to a porphyria clinic. But the referral was denied because their porphyria levels were not high enough. This just shows how tricky it can be to get a clear answer. It is, honestly, a real challenge for some people.
Symptoms That Can Be Tricky
The symptoms of porphyria can be quite varied. They can include things like stomach pain, nerve problems, or skin issues. But here's the thing: these symptoms are also common in many other conditions. For instance, someone thought they had porphyria because of certain symptoms. It turned out, however, they had three different pelvic venous compressions instead. This is a very different problem, obviously.
This overlap makes it hard for doctors to pinpoint porphyria quickly. They have to rule out many other possibilities first. It means a lot of testing and, sometimes, a lot of waiting. This can be very frustrating for people who are feeling unwell and just want answers. It is a bit of a puzzle for medical professionals.
Because the symptoms are so similar to other common illnesses, it takes a keen eye and often specialized tests to tell the difference. This is why persistence in seeking a diagnosis is key. It is, you know, a marathon, not a sprint.
The Path to a Diagnosis
So, what does the diagnostic path usually look like? After seeing your primary doctor, you will likely be referred to someone who knows more about rare conditions. This could be a specialist at a major medical center, like Mayo Clinic, for example. Getting appointments at such places can take some time, as one person mentioned.
Doctors will often order specific tests to measure porphyrin levels in your urine or blood. These tests are crucial for identifying the chemical buildup. If those levels are not high enough, even if symptoms are present, it can complicate the referral process to specialized clinics. This shows how precise the diagnostic criteria can be.
It's a process of elimination and specific testing. It really requires patience from the person seeking help. You might have to go through several steps before getting a clear answer. This is just how it is with rare conditions, often.
Genetic Testing and Specialized Care
Once porphyria is suspected, genetic testing often becomes a very important step. This kind of test can confirm the specific gene change causing the condition. One person mentioned having a porphyria genetic test form and hoping their general practitioner would fill it out. This shows how central genetic testing is to confirming the diagnosis and understanding the specific type of porphyria.
Specialized clinics, like a porphyria clinic, are set up to handle these complex cases. They have the expertise and the tools to manage the condition. Even getting into these clinics can be a process, as one person noted about getting appointments at Mayo Clinic. But once established, these clinics offer comprehensive care.
These specialized centers are vital for managing a rare and complex condition like porphyria. They provide access to the latest treatments and research. They also help families understand the genetic aspects. You can learn more about genetic testing on our site, and we also have information on finding specialized care.
Treating Porphyria: What You Should Know
Treatment for porphyria depends very much on the specific type someone has. For some forms, like Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT), treatments are quite effective. The standard treatment of individuals with PCT is well-established. It aims to reduce the porphyrin buildup and manage symptoms. This is, in a way, very reassuring for those with this particular form.
For other types, especially acute hepatic porphyrias, treatments focus on preventing and managing attacks. As mentioned, new medications like Givlaari are helping to reduce the frequency of these attacks. This is a significant step forward for those who suffer from acute episodes. It is, you know, a real relief for many.
Managing porphyria also involves avoiding triggers that can cause attacks. These triggers can include certain medications, alcohol, or even stress. So, treatment is not just about medicine; it is also about lifestyle adjustments. This is why a comprehensive approach to care is so important. It is a condition that requires ongoing attention.
Living with porphyria means working closely with your healthcare team. This includes regular check-ups and monitoring. The goal is to keep porphyrin levels in check and to prevent serious complications. It is a long-term commitment to health, basically, for the individual.
Common Questions About Porphyria (FAQs)
Here are some questions people often ask about porphyria:
How do you get porphyria?
Porphyria is a genetic condition. You get it when you inherit specific gene changes from your parents. These changes affect the body's ability to make heme properly. Sometimes, though, the condition can appear without a clear family history, which we call sporadic forms. So, it is mostly about your genes, you know, what you inherit.
What are the first signs of porphyria?
The first signs of porphyria can vary greatly depending on the type. They might include stomach pain, sensitivity to sunlight causing skin issues, or nerve problems like weakness. Because these symptoms are common to many other illnesses, they can be tricky to spot as porphyria. It is, you see, why diagnosis can take time.
Is porphyria a genetic disease?
Yes, porphyria is indeed a genetic disease. It comes from inherited changes in genes that control the production of heme. These gene changes lead to the buildup of porphyrins in the body. While environmental factors can sometimes trigger symptoms, the underlying cause is genetic. It is a condition that runs in the family, or sometimes, it is a new genetic change.
Where to Learn More
If you are interested in learning more about porphyria, there are many resources available. For more detailed medical information, you might visit a trusted health resource like the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). They offer a lot of useful information. It is a good place to start your research.
Remember, getting good information is important when dealing with rare conditions. Knowing the facts can help you understand the situation better. It can also help you talk to your doctors more effectively. So, keep learning, that is a good thing to do.
This information is current as of November 2023. Medical understanding of conditions like porphyria is always advancing. For the most up-to-date advice, always talk with a healthcare professional. They can give you the best guidance for your unique situation. It is, after all, their area of deep knowledge.
We hope this has cleared up the question about whether porphyria comes from inbreeding. It is a common query, but the truth about porphyria's genetic origins is a bit more nuanced. Understanding this helps us focus on what truly matters: getting the right diagnosis and finding the best ways to manage this condition.

Detail Author:
- Name : Mr. Chester Koch PhD
- Username : ukihn
- Email : ellie61@yahoo.com
- Birthdate : 1977-12-14
- Address : 7304 Boehm Mall Apt. 703 Hayleemouth, ID 68818
- Phone : (302) 820-0617
- Company : Turner, Hirthe and Goyette
- Job : Foundry Mold and Coremaker
- Bio : Quia est et dolore. Quae ea voluptatum alias libero. Incidunt velit sed porro deleniti enim omnis suscipit. Vitae eos beatae sit deleniti ipsa.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/gerald.wilderman
- username : gerald.wilderman
- bio : Dolor et ducimus itaque rerum suscipit aut maxime. Quibusdam sit inventore occaecati. Soluta perspiciatis aut et voluptatem ut.
- followers : 5509
- following : 2368
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/gerald_xx
- username : gerald_xx
- bio : Est quidem voluptatem ab iusto minima.
- followers : 1820
- following : 1115
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/gerald_real
- username : gerald_real
- bio : Sit quis sit est accusamus aut incidunt vitae.
- followers : 4123
- following : 1975

